- Hash pointers
Usually, an ordinary pointer is used to store a data address in the computer’s memory. However, a hash pointer isn’t only used to store the address, but also used to store the hash value of the data. Therefore, we can detect if the data is tampered with.
- What is block chain?
Commonly speaking, a block chain is a chain list of blocks connected one by one. But one of the biggest differences between the block chain and the ordinary link list is that the ordinary pointers are replaced with the hash pointers.
The following diagram is a simple block chain.
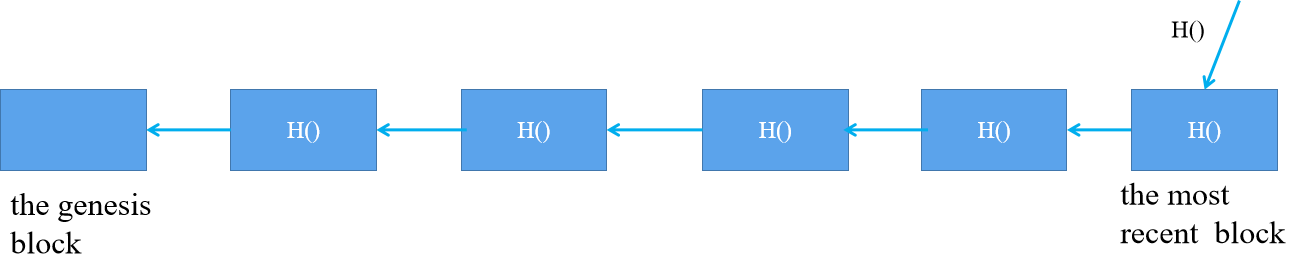
The first block is called the genesis block, the last is called the most recent block. Each block has a hash pointer that points to the previous block except the genesis block, the last block’s hash pointer is stored in the system. The hash pointer is calculated from hashing the previous block including the hash pointer in the block. By adopting the data structure, we can implement the tamper-evident log. If an attacker changes a block record, all hash pointers behind the tampered block will be changed including the latest block’s hash pointer. However, the hash pointer of the latest block is stored in the system. In a word, we can detect any changes easily in the block chain, because any changes in the block will lead to a change of the latest block’s pointer to occur. Based on this feature, some nodes in Bitcoin can only store the latest batch block information and these nodes are named light nodes, while others that possess full blocks information are named full nodes. When some blocks’ information is used, they can apply for the information from others with full blocks information. But how to know the information applied from others is true? To solve the problem, the above anti-tampering feature is used.
Merkle tree and binary tree
One of the biggest differences between the Merkle tree and the binary tree is that the ordinary pointers are replaced with hash pointers.
The following diagram is a simple Merkle tree.
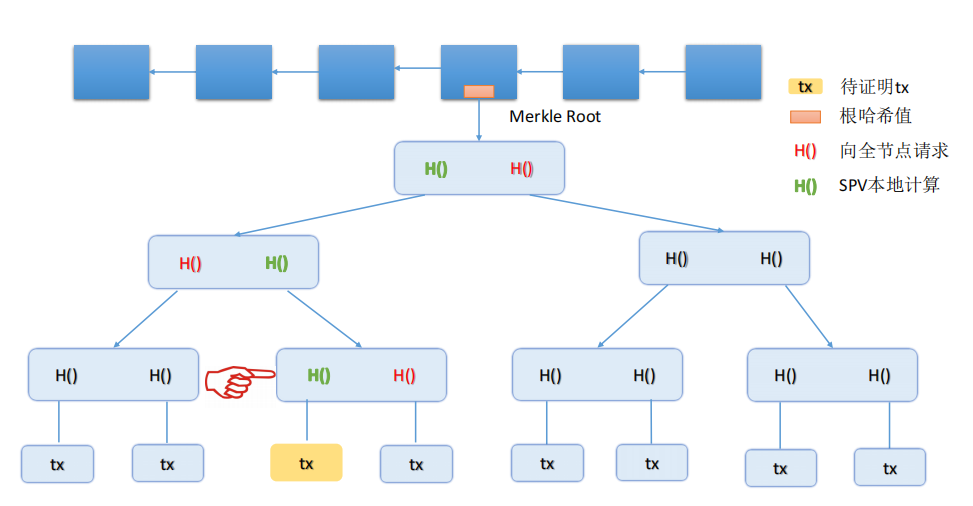
All layers are hash pointers layers except the bottom layer called the data blocks layer. Similar to the previous descriptions, a node in Bitcoin only possesses the root hash value, it can easily detect any changes in the block chain. Because any tampering with the block record will cause a change of the Merkle root hash value to occur. Therefore, one of the effects of the Merkle is to provide Merkle proof.
A data block in the data blocks layer contains some transactions. Every block is composed of a block header and a block body. The block header contains the hash value of a Merkle tree root, the Merkle tree’s root is the block. The transactions list is included in the block body.
Merkle Proof
How do light nodes prove if a transaction was written to the block chain?
As shown in the diagram above, the yellow block contains the transaction waiting to be proven, and the path with red hash values and green hash values is the Merkle proof. The red hash values are absent in the diagram, while green hash values can be calculated by the light node itself. When a light node wants to prove whether the transaction was written to the block chain, it will request the red hash values from full nodes. After the light node receives the green hash values, it can calculate the all green hash values from bottom to top. Finally, it will get the Merkle tree root hash value by calculating. If the value is equal to the Merkle tree root hash value that the light node stores, the transaction was written to the block chain. Otherwise, the transaction is spurious.
Reference
- Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Technologies A Comprehensive Introduction [Arvind Narayanan, Joseph Bonneau, Edward Felten, Andrew Miller, Steven Goldfeder]
- http://zhenxiao.com/blockchain/
文档信息
- 本文作者:wendaocsmaster
- 本文链接:https://wendaocsmaster.github.io/2023/02/16/block-chain-Data-structure-in-Bitcoin/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)